
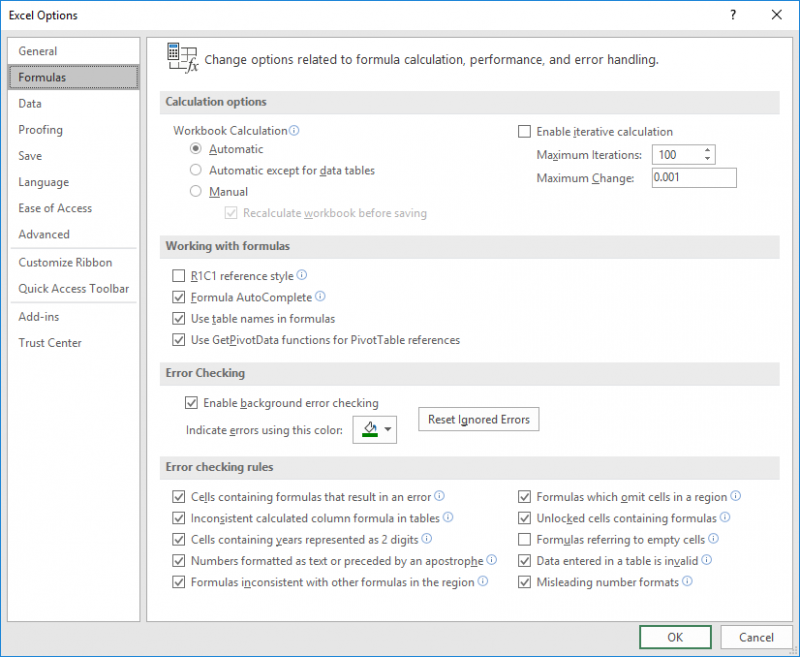
You can also introduce other functions in the IF statement to make calculations like the AVERAGE function. You need to make the cell reference of average monthly sales as an absolute value by using $ sign in the above IF statement so that this cell reference does not change when you copy the formula to other rows. =IF(B5>$B$2,"Above Average","Below Average") You need to calculate the average monthly sales using the AVERAGE function for comparison purpose, say in cell B2, and you need to compare each salesperson’s sales amount with this average monthly sales figure using IF function, such as Numbers are always logically tested using comparison operators in IF function, like Greater Than (>), Greater Than Equal to (>=), Less Than () and based on TRUE and FALSE results some specified values are returned.įor example, you have sales data of salespersons for a particular month and you need to compare each salesperson’s sales amount against average monthly sales and return resulting values, like “ Above Average” or “ Below Average”.
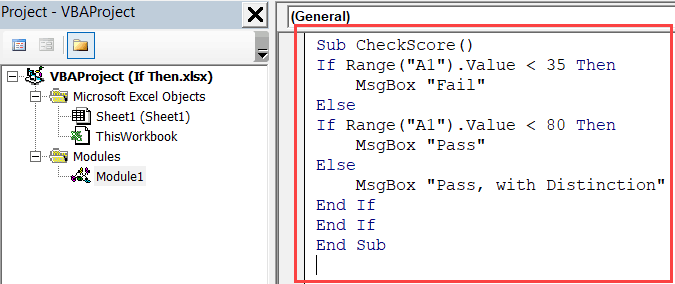
If you want to return numeric values or logical test values as TRUE and FALSE in value_if_true and value_it_false arguments, then you do not need to enclose in double quotation marks, such as =IF(B2>60,1,0).If you don’t supply the value_if_false argument, and use only a closing bracket followed by the value_if_true argument, then the IF function returns FALSE, such as =IF(B2>60,"Good").If you forget to supply the value_if_true argument in the IF function and use only a comma followed by the logical_test argument, then the IF function returns zero (0) for the True argument part, such as =IF(B2>60,"Bad").While using the IF function, you need to follow a few rules. In simple words, it says, that if a number is greater than a certain number, then return “ Pass,” otherwise return “ Fail.” Some Rules to follow with the IF function It is also optional.īy following this syntax, you perform a logical test or condition on a value, and return a specified value if logical test is TRUE, else return another value if logical test is FALSE. Value_if_false – It is a value to be returned when logical_test is FALSE. Value_if_true – It is a value to be returned when logical_test is TRUE. Logical_test – It is logical comparison or condition that is tested as TRUE or FALSE. In Excel it has following syntax to follow The IF statement has two parts first IF a comparison or condition is TRUE, and second IF a comparison or condition is FALSE. This is a powerful feature once you’ve learned the basics of constructing a statement. This function is used to test logical comparisons or conditions on a value. Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.The IF function is one of the most popular and widely used functions in Excel. Other keywords used in declarations are ReDim, Static, Public, Private, and Const. Dim statements are one type of statement used to declare variables. You can declare a variable to be any object that is exposed in the application that you are using.
The data type is an object, in this case, a Microsoft Excel Range object. The Dim statement declares the m圜ell variable. The Const statement declares the constant limit specifying the Integer data type and a value of 33. All the statements enclosed by the Sub and End Sub statements are executed whenever the ApplyFormat procedure is called or run. The Sub statement (with matching End Sub statement) declares a procedure named ApplyFormat. The following example contains three declarations. When you declare a procedure, variable, or constant, you also define its scope, depending on where you place the declaration and what keywords you use to declare it. You use declaration statements to name and define procedures, variables, arrays, and constants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
